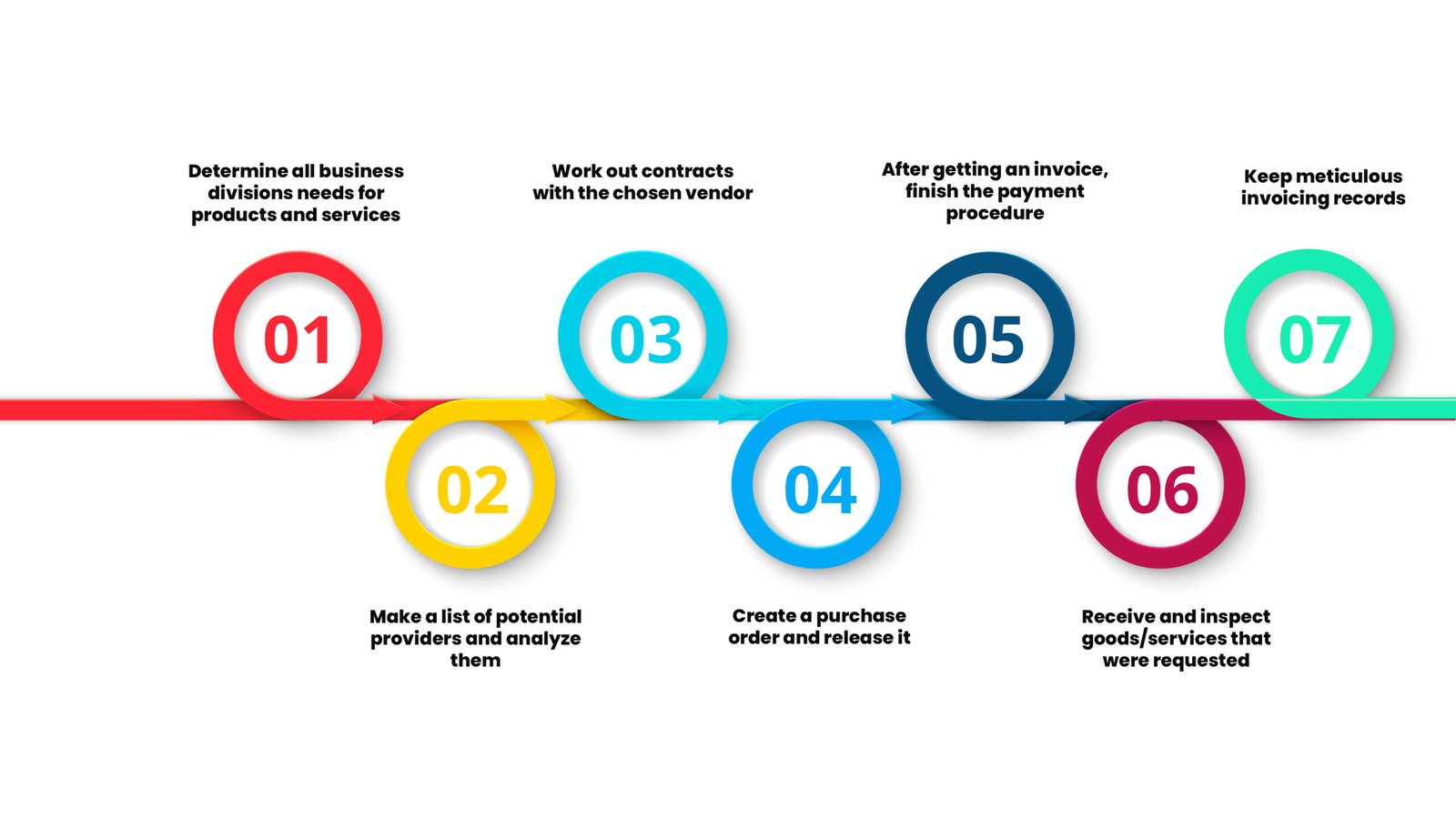
The 7 Steps to a Successful Procurement Process
The following are the 7 steps to a successful procurement process:
Step 1: Determine the items and services that each business division needs
The procurement cycle starts when any business unit of an organisation needs products or services from an outside source. As a result, identifying and combining the demands of multiple business divisions within an organisation constitutes the first step in the procurement process. By having visibility into your spending areas and categories, you may use spend analysis to identify areas for cost-cutting.
Step 2: Make a list of potential providers and evaluate them
The next step is to create a list of potential suppliers who could offer the goods or services after the business units’ needs have been determined. In this process, basic online searches or more official actions like RFPs, RFQs, and RFIs are used.
This process’ objective is to evaluate possible suppliers. Some of the evaluation criteria include costs, service quality, industry reputation and awards, warranty and guarantee terms, and customer service. Following the evaluation, the provider who offers the greatest value and the most competitive pricing is given the contract.
Step 3: Settling on contracts with the selected vendor
When a provider has been selected to satisfy an organization’s needs, the contract process starts. Contracting is a crucial step for every firm to generate value as efficiently as possible and to encourage supplier-buyer cooperation. This process comprises assessing crucial components including the cost structure, the nature of the task, the terms and conditions, and the due dates, among others. Through careful contract analysis and negotiation, it is possible to find further cost-cutting possibilities, such as dynamic discounting.
Step 4: Create a purchase order and release it
After a business has signed its contract with a supplier, the following step is to create a buy requisition (PR). A PR offers details on the product or service, its cost and quantity, the provider’s identity, and the approval procedure.
A purchase order (P)O, which includes details such as the PO number, payment terms, and supplier information, is sent to the supplier when a PR is approved by the finance team.
Step 5: Complete the payment process after receiving an invoice
Upon receiving a PO, a supplier will issue an invoice outlining the cost of the requested goods or services. When the company gets and bills the PO, the procurement team compares it to the PO to ensure quality and quantity.
Depending on the payment terms agreed upon by the organisation and its suppliers, money is either given before or after delivery.
Step 6: Collect the specified items and services and examine them
According to the conditions of the contract and payment, the provider offers the products or services. Upon receipt, businesses should inspect their suppliers to ensure that they have met their quality standards.
Step 7: Maintain exact invoice records
It is crucial to properly maintain all invoices after receiving a delivery to keep track of spending and the many categories of corporate expenses.